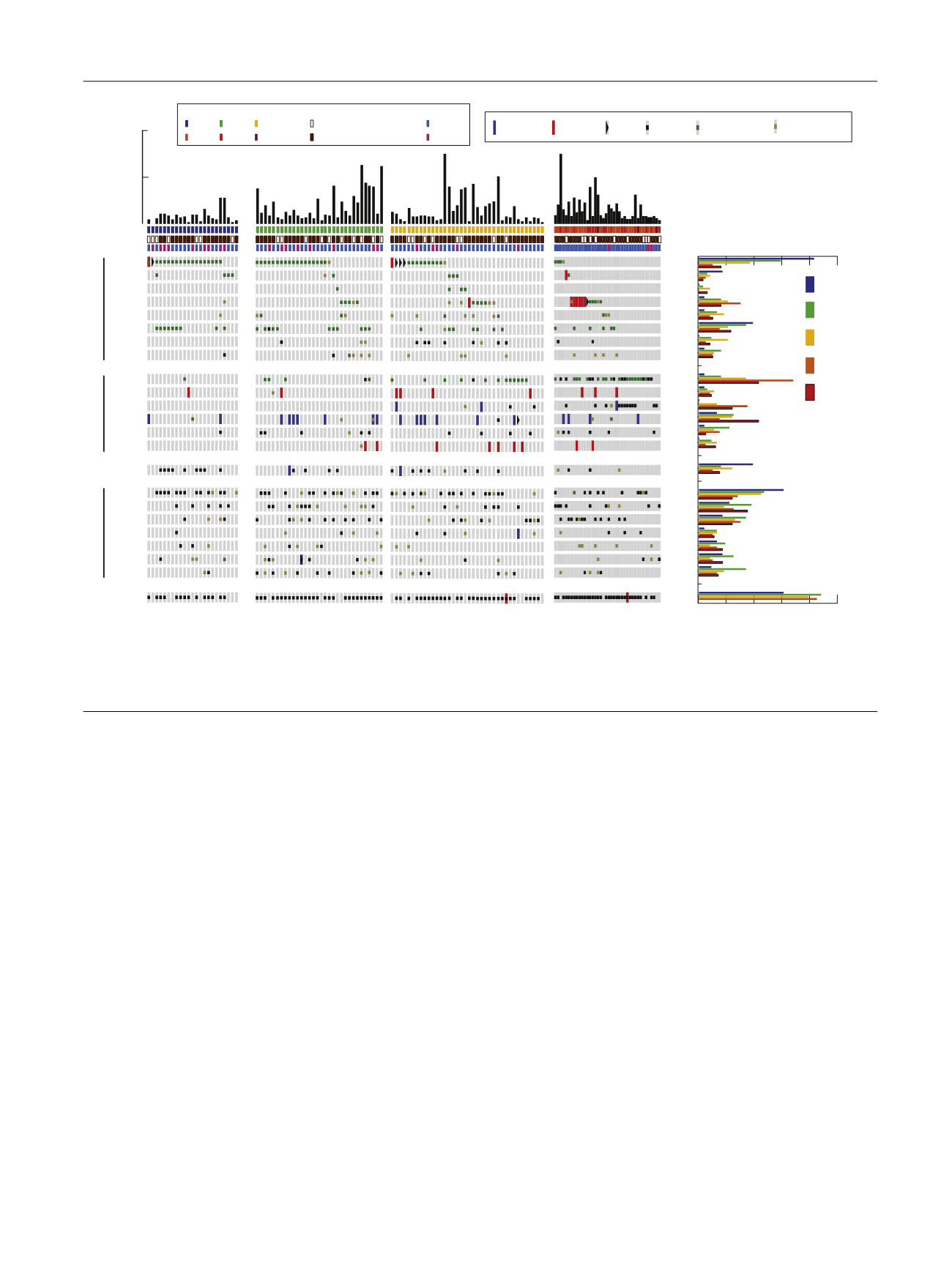
Interestingly, mutations in
ERBB2/HER2
were identified in
amutually exclusive patternwith alterations in
FGFR3
( Fig. 1,
Supplementary Table 7, Supplementary Fig. 6). With the
exception of a single LGTa tumor that harbored an
ERBB2
missense mutation of unknown significance (R103Q),
ERBB2
alterations were only present in high-grade NMIBC tumors.
Six of the 12 Tis specimens analyzed had
ERBB2
alterations,
includinghotspot S310Fmissensemutations in three tumors,
amplification in one, and mutations of unknown significance
in two tumors (S728F and S305C, respectively).
ERBB2
alterations were associated with higher grade (
p
= 0.01)
and stage (
p
= 0.05) but not after adjusting for multiple
genomic comparisons (
p
= 0.60 and
p
= 0.20, respectively).
While
FGFR3
was associated with lower-grade and lower-
stage disease, alterations in
FGFR3
were seen in39% (32/82) of
high-grade NMIBC. In total, 57% (47/82) of high-grade NMIBC
tumors had alterations in either
ERBB2
or
FGFR3
, suggesting
that trials testing targeted inhibitors of these kinases should
be further explored (Supplementary Fig. 7A).
An alteration in either the TP53 pathway or a gene with a
central role in cell cycle regulation was identified in 47%
(49/105) of NMIBC tumors, most commonly in high-grade
tumors
( Fig. 1 ,Supplementary Fig. 8). An expected stepwise
increase in
TP53/MDM2
alteration rates were seen with
stage (
p
<
0.001) and grade (
p
<
0.001) from 9% in LGTa
(2/23), 19% in HGTa (6/32), 45% in HGT1 (17/38), and 75% in
MSK-MIBC (30/40). Furthermore, alterations in cell cycle
regulation genes (
RB1
, Cyclin D1 [
CCND1
],
CDKN1A
[p21], or
CDKN2A
) were more common in higher stage (
p
= 0.028)
and grade (
p
= 0.009) disease, increasing from 13% in LGTa
(3/23), to 41% in HGTa (13/32), 42% in HGT1 (16/38), and
53% (21/40) in MSK-MIBC (Supplementary Fig. 8).
3.4.
DNA damage repair and mutational burden
As recent reports suggest that DNA damage repair (DDR)
gene alterations are associated with sensitivity to cisplatin,
immunotherapy, and radiation therapy in MIBC
[18–20], we
assessed the prevalence of alterations in these genes in
NMIBC. Deleterious DDR gene alterations were identified in
30% (25/82) of high-grade NMIBC tumors, but in only 4%
(1/23) of low-grade tumors (
p
= 0.012;
Fig. 2 A). This rate of
deleterious DDR gene alterations in high-grade NMIBC was
similar to the MSK-MIBC cohort (33% [13/40]).
ERCC2
missense mutations were the most common DDR gene
alteration, occurring in 17% (14/82) of high-grade NMIBC
tumors and 20% of MSK-MIBC (8/40). As has been shown in
MIBC, the majority of missense mutations in NMIBC were
FGFR3
KRAS
HRAS
ERBB2
ERBB3
PIK3CA
TSC1
NF1
TP53
MDM2
RB1
CDKN2A
CDKN1A
CCND1
STAG2
KDM6A
KMT2D
ARID1A
KMT2A
KMT2C
EP300
CREBBP
TERT
Promoter
Female
Male
Never smoker
Former or current smoker
Low-grade Ta
(
n
= 23)
High-grade Ta
(
n
= 32)
High-grade T1
(
n
= 38)
High-grade T2-T4
MSK-IMPACT MIBC
(
n
= 40)
0
20
40
60
80
100
0
20
40
60
80
100
FGFR3
KRAS
HRAS
ERBB2
ERBB3
PIK3CA
TSC1
NF1
TP53
MDM2
RB1
CDKN2A
CDKN1A
CCND1
STAG2
KDM6A
KMT2D
ARID1A
KMT2A
KMT2C
EP300
CREBBP
Low grade Ta
High grade Ta
High grade T1
MSK-IMPACT
MIBC (T2-T4)
TCGA
MIBC (T2-T4)
Mutation count on MSK-IMPACT
100
50
RTK - PIK3 pathway
TP53/Cell cycle pathway
Chromatin-modifying genes
Stage/Grade
Tobacco
Gender
Sex
Tobacco
Stage/Grade
LG Ta HG Ta HG T1
HG T2 HG T3 HG T4
TERT
Promoter
Frequency of genomic alterations
Amplification
Deep deletion
Recurrent
Missense mutation
Truncating
Mutation
Fusion
Novel
Missense mutation
Fig. 1 – An overview of the genomic landscape of NMIBC by grade and stage with comparison to MIBC.
HGTa = high-grade Ta; LGTa = low-grade Ta; MIBC = muscle invasive bladder cancer; MSK-IMPACT = Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center-Integrated
Mutation Profiling of Actionable Cancer Targets; NMIBC = nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer; TCGA = The Cancer Genome Atlas.
E U R O P E A N U R O L O G Y 7 2 ( 2 0 1 7 ) 9 5 2 – 9 5 9
955