3.2.
Genomic landscape of NMIBC
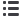
The most frequently altered genes in NMIBC were the
TERT
promoter (73%),
FGFR3
(49%),
KDM6A
(38%),
PIK3CA
(26%),
STAG2
(23%),
ARID1A
(21%), and
TP53
(21%)
( Fig. 1 ,Supplementary Figs. 2 and 3, Supplementary Table 4).
The associations between genetic alterations with tumor
stage and grade are presented in Supplementary
Tables 5 and 6.
TERT
promoter mutations were identified
in 61% (14/23) of LGTa, 88% (28/32) of HGTa, and 79% (30/
38) of HGT1 tumors. The
TERT
promoter region was not
sequenced by TCGA, as the whole-exome sequencing
method employed interrogated only protein-coding
regions. However,
TERT
promoter mutations were identified
in 85% (34/40) of the MSK-MIBC patients.
TERT
promoter
mutations were present at similar frequency across stage
(
p
= 0.2) and grade (
p
= 0.15).
Alterations in chromatin modifying genes were also
highly prevalent in NMIBC, occurring in 69% (72/105) of the
tumors
( Fig. 1, Supplementary Fig. 4). The most commonly
altered chromatin-modifying genes were
KDM6A
(38%) and
ARID1A
(21%).
KDM6A
was altered in 52% (12/23) of LGTa,
38% of HGTa (12/32), 32% (12/38) of HGT1, and 25% (10/40)
of MSK-MIBC, and 24% of TCGA-MIBC tumors.
ARID1A
mutations were identified in 9% (2/23) of LGTa, 28% (9/32)
of HGTa, 18% (7/38) of HGT1, 30% (12/40) of MSK-MIBC, and
24% of TCGA-MIBC tumors. While
KDM6A
alterations were
identified more often in LGTa, there were no statistically
significant associations with grade (
p
= 0.15) or stage
(
p
= 0.44). Similarly,
ARID1A
mutation did not correlate
with either grade (
p
= 0.23) or stage (
p
= 0.44).
Another frequently altered gene was
STAG2
, present in
23% of the NMIBC cohort (LGTa = 39% [9/23]; HGTa = 16%
[5/32]; HGT1 = 24% [9/380], 5% of MSK-MIBC [2/40], and
15% of TCGA-MIBC;
Fig. 1 ). Studies are conflicted over
whether
STAG2
mutations are associated with aneuploidy
and aggressive bladder tumors or associated with lower
grade and l-stage disease
[10,11,13,14] .We found truncat-
ing
STAG2
mutations in our cohort to be associated with
LGTa tumors (
p
= 0.046).
3.3.
Genomic pathways of NMIBC
To better define the prevalence and co-occurrence patterns
of potentially actionable genomic alterations in NMIBC, we
analyzed known cancer-associated genes within the context
of their canonical pathway and cellular function. Alterations
in the receptor tyrosine kinase/phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase pathway were present in 79% (83/105) of NMIBC
tumors
( Fig. 1 ,Supplementary Fig. 5). Consistent with
previous studies,
FGFR3
mutations were associated with
lower grade and stage (LGTa = 83% [19/23]; HGTa = 59% [19/
32]; HGT1 = 34% [13/38]; MSK-MIBC = 8% [3/40]; TCGA-
MIBC = 16%)
[5]. Four
FGFR3
fusions were identified in the
NMIBC cohort, including a
FGFR3-TNIP2
fusion predicted to
be activating due to its in-frame
FGFR3
kinase domain and a
recent NGS report identifying another bladder tumor with a
FGFR3-TNIP2
fusion
[15] .We also identified a
FGFR3-TACC3
fusion in a LGTa tumor. While
FGFR3
fusions have
predominantly been reported only in high-grade tumors,
there are a few low-grade
papillary
bladder cell lines known
to harbor
FGFR3-TACC3
fusions
[16,17].
Table 1 – Clinicopathologic characteristics of NMIBC cohorts
Characteristics
Low-grade
NMIBC (%),
n
= 23
High-grade
NMIBC (%),
n
= 82
High-grade NMIBC treated BCG
without maintenance (%),
n
= 62
Median age (range)
67 (25, 80)
70 (36, 87)
69.8 (37.3, 87.3)
Sex
Male
13 (56)
67 (82)
51 (82)
Female
10 (43)
15 (18)
11 (18)
Smoking
Current
3 (13)
13 (16)
9 (15)
Former
13 (57)
46 (56)
35 (56)
Never
7 (30)
23 (28)
18 (29)
Stage
Ta
23 (100)
32 (39)
26 (42)
Tis
0
12 (15)
12 (19)
T1
0
38 (46)
24 (39)
No. of tumors
Single
18 (78)
45 (55)
33 (53)
Multiple
5 (22)
37 (45)
29 (46)
Tumor size (cm)
<
3
16 (70)
46 (56)
36 (58)
3
7 (30)
36 (44)
26 (42)
Concomitant CIS
No
23 (100)
43 (52)
30 (48)
Yes
0 (0)
39 (47)
32 (52)
Treatment
BCG
3 (13)
66 (80)
62 (100)
MMC
9 (39)
1 (1)
0 (0)
Observation
11 (48)
10 (12)
0 (0)
Immediate cystectomy
0 (0)
5 (6)
0 (0)
BCG = bacillus Calmette-Gue´rin; CIS = carcinoma in situ; MMC = mitomycin; MIBC = muscle invasive bladder cancer; NMIBC = nonmuscle invasive bladder
cancer; TUR = transurethral resection.
E U R O P E A N U R O L O G Y 7 2 ( 2 0 1 7 ) 9 5 2 – 9 5 9
954